[ad_1]
Health risks from heat waves were characterized by rapid growth, nonlinear temporal evolution, and extremity. Nationally, the number of annually attributable deaths averaged 3,679 in the 1980s but rose to 15,500 in the 2010s. Using a 5-year rolling average, it took 2.8 years for each increase in 1,000 annual heatwave-related deaths from 1980 to 2000, but only one year for the same increase in the 2010s. Attributable deaths also hit the highest record in 2017 at 26,486, followed by the second 21,219 in 2019 and the third 20,431 in 2013. Regionally, east and central China generally had the largest number of attributable deaths, accounting for more than 50%. of deaths nationwide. Among provinces, heatwave-related deaths were highest in Shandong, followed by Henan, Hebei and Jiangsu. (ad) The number of heatwave-related online deaths over the past four decades. (e) Deaths attributable to heat waves in China from 1979 to 2020. The solid line shows the estimated number of deaths attributable to heat waves; gray areas show the 95% confidence intervals; The horizontal dashed line shows the average annual deaths in the 1980s, 1990s, 2000s, and 2010s. (f) Changes in deaths attributed to heat waves in the 2010s compared to the base period 1980-2009. AD, deaths attributed to heat waves. Photo credit: Huiqi Chen/Science China Press
This study is led by Dr. Cunrui Huang (Vanke School of Public Health, Tsinghua University). Heat waves cause a heavy disease burden by increasing the risk of mortality and morbidity, which has been exacerbated by global climate change. “In China, evidence documenting the impact of heat waves on the number of attributable deaths, spatio-temporal variability, and their driving factors is still limited, hampering understanding of dangerous heat waves,” says Huang.
Huang, along with his group member Chen and meteorology expert Zhao, tried to find out the spatial and temporal trends of heatwave-related deaths in China over the past four decades. The team performed event-based attributable loss estimation to quantify the gridded attributable deaths.
The team found that health risks from climate change were characterized by rapid growth, nonlinear evolution, and extremity. Heatwave-related deaths in China have increased dramatically by four times over the past four decades, with rising trends becoming more apparent over the past decade but with some year-to-year fluctuations. Regionally, east and central China generally had the most attributable deaths and accounted for more than 50% of deaths nationwide. Among provinces, heatwave-related deaths were highest in Shandong, followed by Henan, Hebei and Jiangsu.
The researchers also dissected the factors driving changes in attributable deaths. The rise in heatwave-related deaths in China over time was mainly due to increased heatwave exposure, followed by growth of population, population aging and rising primary mortality. Above all, aging population has played an increasingly important role in attributable deaths over time. This work could provide important information for Politician Developing effective mitigation and adaptation responses to increasing heat waves, particularly for the most vulnerable elderly populations.
The study was published in science bulletin.
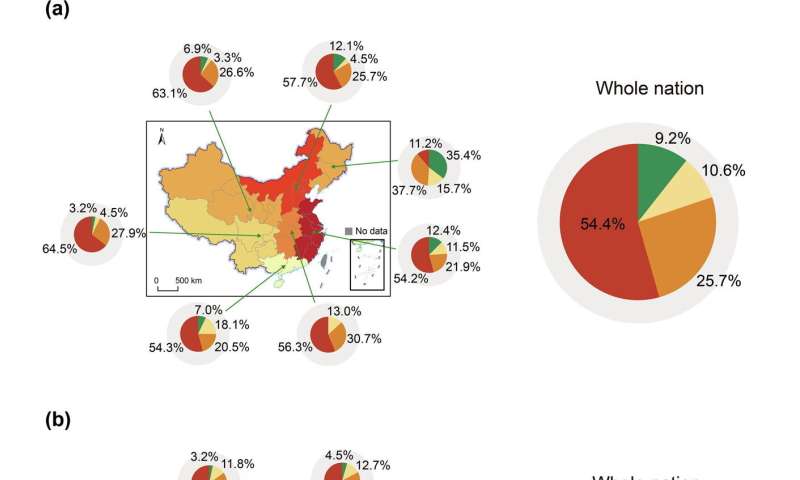
The increase in heatwave-related deaths in China was primarily due to increased heatwave exposure, followed by population growth, population aging and rising baseline mortality. In particular, population aging has played an increasingly important role in attributable deaths over time, increasing from 10.6% in the period 1980-1990 to 15.8% thereafter, and even 20 in the period 2000-2010, has reached 8%. (a) Decomposition of the contribution of driving factors in seven regions (left) and for the whole nation (right) from 1980 to 1990. (b) Decomposition of the contribution of driving factors in seven regions (left) and for the whole nation (right). ) from 1990 to 2000. (c) Decomposition of the contribution of driving factors in seven regions (left) and for the entire nation (right) from 2000 to 2010. AD, Heat-wave-related deaths. Photo credit: Huiqi Chen/Science China Press
Huiqi Chen et al., Spatial-temporal variation in mortality burden from heat waves in China, 1979–2020, science bulletin (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.scib.2022.05.006
Provided by
Science China Press
Citation: Investigating the Spatio-Temporal Variation in Mortality Burden from Heat Waves in China, 1979-2020 (2022, September 2), retrieved September 5, 2022 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2022-09-spatiotemporal-variation -mortality-burden- attributable.html
This document is protected by copyright. Except for fair trade for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is for informational purposes only.
[ad_2]
Source link